MAS Holdings drives 13-point gain in board diversity through gender-equity strategy
Start Reading

1. Company at a Glance
In this case example, we'll explore how MAS Holdings engaged in active interventions to address the challenge of closing the gender leadership gap with a comprehensive, multi-dimensional strategy. Despite facing significant obstacles, the company set bold goals, including achieving 30% gender representation in management by 2025. By integrating accountability frameworks, securing leadership commitment, and fostering cultural shifts, MAS implemented lasting change, leading to measurable improvements in women’s representation and a more inclusive organizational culture.
51 manufacturing facilities across 10 countries, with its biggest markets in the United States, Europe, and Asia
Global presence
2. The Challenge
Female Leadership Underrepresentation
MAS Holdings operates in a predominantly female-driven industry; however, there has been a stark underrepresentation of women in leadership roles. By 2018, female representation on the company’s main Board of Directors was just 8%, highlighting a significant gender parity gap at the top. The company also faced cultural, social, and economic barriers that limited women’s opportunities for advancement.
In 2019, MAS Holdings set a bold target: to achieve 30% gender representation in management by 2025. This goal was not only about addressing gender equality but also about strengthening the company’s business strategy, as diverse leadership teams were identified as key drivers of innovation, collaboration, and overall business success.
3. The Action
How MAS Holdings is bridging the leadership gap
To advance gender equality and achieve its ambitious goals, MAS Holdings implemented a comprehensive, multi-pronged strategy focused on mindset, training, childcare support, policy, and accountability.
Building the Foundation for Progress Through Education
Changing Mindsets Through Workshops
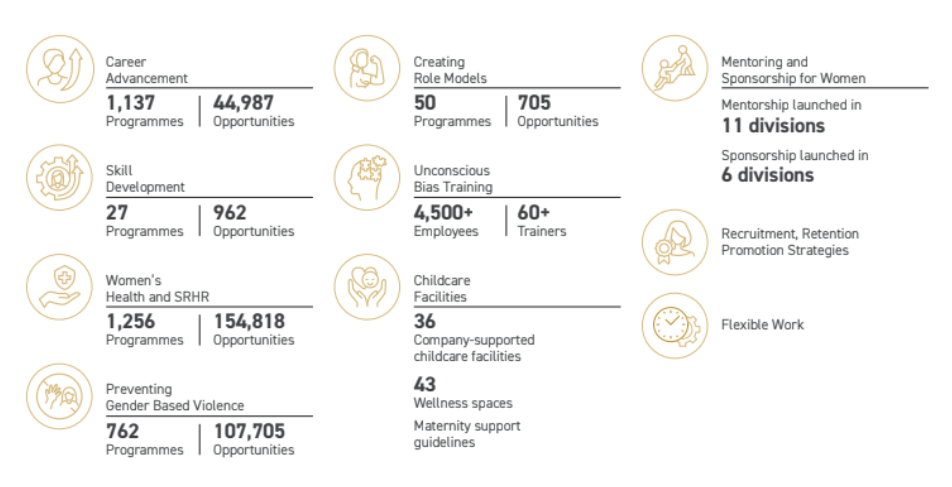
MAS Holdings initiated a cultural shift by introducing sensitization workshops across the organization. These workshops aimed to educate employees, starting with senior leaders and eventually reaching middle management and the wider workforce. The sessions focused on the business benefits of diversity, building a truly accessible workplace, and addressing unconscious bias. By fostering open conversations and challenging ingrained stereotypes, MAS sought to create an inclusive environment where diversity was embraced as a strength.
Women Go Beyond Program
This flagship program equips women with skills and knowledge to advance their careers while addressing personal well-being.
Childcare Support & Flexible Work
To support the needs of working parents, as of 2024, MAS offered childcare assistance in 36 locations worldwide, providing direct benefits to over 500 children. Additionally, the company conducted surveys to assess employees' needs and improve these services further. Recognizing the importance of work-life balance, MAS also implemented flexible work arrangements and paternity leave. These measures sought to encourage greater participation from men in family responsibilities, shifting societal norms and alleviating the pressures traditionally placed on women.
Reforming Recruitment and Talent Pipeline Policies and Support
MAS undertook significant policy reforms to address systemic barriers to gender equality. Recruitment and communication practices were transformed to ensure they were not merely gender-neutral but actively gender-transformative, taking into account the uneven playing field women often face. Structured mentorship and sponsorship programs were launched to connect women in executive roles with senior leaders and to pair managerial-level women with board members. These initiatives aimed to inspire and equip women to pursue leadership positions, fostering a stronger presence in decision-making bodies.
Establishing an Accountability Framework & Data
Accountability was central to MAS’s approach, which is why the company assigned specific gender representation targets to business and HR leaders, holding the senior leadership accountable. These targets were based on the existing baseline, making it easier to measure progress against ongoing actions. By holding leaders responsible for driving progress, MAS integrated diversity objectives into its core operations, ensuring sustained focus and measurable outcomes over time. Data is central to this and they developed a robust and regularized system to track progress.
4. Overcoming Barriers
While MAS made significant progress, the journey was not without its challenges. These obstacles, however, became opportunities for meaningful reflection and dialogue within the organization.
Resistance to Change
Initially, there was considerable resistance to flexible work arrangements, particularly from leaders within the manufacturing sector who viewed these policies as incompatible with the nature of the industry. This resistance underscored the difficulty of changing deeply ingrained practices. Yet, the global pandemic shifted perspectives, highlighting the viability and benefits of flexible work, ultimately increasing leadership buy-in and acceptance.
Cultural and Societal Norms
Operating in regions with strong traditional gender roles, MAS faced external and internal challenges in promoting women’s leadership. Many employees were unfamiliar with the business case for gender equality, and the company had to invest in education to shift mindsets. The journey required addressing both overt resistance and more subtle, unconscious biases that often went unchallenged in the workplace.
Unconscious Gender Biases
Unconscious gender biases shaped hiring and promotion practices, limiting women’s advancement into leadership positions. MAS worked to mitigate this through sensitization workshops, leadership training, and adjusting recruitment practices. However, these changes took time to take root, and addressing bias at every level of the organization remained a long-term challenge.
5. Impacts & Results
MAS Holdings’ initiatives have yielded measurable progress, despite the challenges posed by the pandemic:

Female representation in management increased from 21% in 2019 to 26% in 2024.

Representation on the Board of Directors grew from 8% in 2018 to 21% in 2024

In 2024, 1,083 fathers have utilized paternity leave
In 2024, over 3,700 mothers were supported not only through provision of maternity leave, but also through provision of additional care, nutritious meals, awareness and education and other provisions such as care packs.
36 global locations providing employer-supported childcare assistance.
48.28% of maternity return rate
In 2024 12% of executive and above cadre were using flexible working arrangements
Increase in the number of women working in some of the facilities as well as decrease in the number of sick leaves
A cultural shift has begun, as evidenced by greater participation and support from male employees in family-focused policies like paternity leave.
MAS Holdings has fostered a more inclusive environment, empowering women and creating pathways for career advancement.
6. Key Lessons Learned
Setting Targets as a Key Starting Point:
It is a lengthy process, but necessary to ensure the right goals are set. MAS Holding spent time researching what local and global organizations were doing in this space and gathering insights from the teams through one-on-ones, focus groups, and leadership meetings. The goal was to understand their perspectives on why these initiatives were necessary.
Leadership Buy-In Drives Organizational Change
Cultural and mindset shifts are equally essential. Leadership commitment and transparent communication are crucial for advancing gender equality. MAS’s leaders not only set the tone but also engaged in transparent communication, making sure employees understood the reasons behind the initiatives.
Support Structures Enable Success
Infrastructure changes, such as childcare support and flexible work policies, address systemic barriers and create an environment where women can thrive professionally without compromising personal responsibilities.
Progress Requires a Long-Term Vision
Sustainable progress requires a persistent focus on education, awareness, and policy adjustments. The journey to equality is continuous and must evolve with the organization’s growth and the changing social landscape.

"Setting targets to hold a company accountable is crucial. However, creating mindset change is equally important. It requires challenging and unlearning centuries of gender-biased socialization and the structures within which the corporate world operates”
Dinali Peiris, Human Resources Director
7. Company Commitment
MAS Holdings is a participant of the UN Global Compact since 2003, including:
Forward Faster Signatory on Climate Action Target 1 (Net-Zero Emissions).
Women Empowerment Principles Signatory since 2011.
Target Gender Equality Accelerator participant (2022).
Climate Ambition Accelerator participants in 2024.
8. Recommended Resources
Inspired to take action? Recommended UN Global Compact resources available to support your journey:

Target Gender Equality Accelerator

Target Setting for Gender Equality

Sign Up to Forward Faster Get to know better MAS gender
Get to know better MAS gender strategy in this interview with Dinali Peiris, Human Resources Director.
Download Case Study
Disclaimer: This case example is intended strictly for learning purposes and does not constitute an endorsement of the individual companies by the UN Global Compact.